How the Toyota 2JZ Became the Company’s Most Influential Engine Option
There are several iconic engines on the market, but few rival the status of the Toyota JZ series. However, the 2JZ engine is easily the most important. Born out of the need to limit the extreme nature of some vehicles, this engine quickly became one of the most durable but also among the most customizable options. Like the 1JZ engine, this has led to it powering some of Toyota’s most revered cars, including the well-respected Supra.
Here’s how the Toyota 2JZ became one of the company’s most influential and revered engine options.
A brief history of the Toyota 2JZ engine
As many car enthusiasts know, the 2JZ came after the Toyota M-Series engine. The iconic Toyota 2JZ engine resulted from a gentlemen’s agreement made by Japanese automakers. At the time, cars were getting a bit extreme, and the thought was that they needed to limit the maximum output for the government not to impose strict regulations. As a result, the collected group of automakers agreed that no production car would exceed a certain horsepower. This agreement was in place until 2005.
According to MotorTrend, the first use of the 2JZ, which existed alongside the 1JZ, came in 1991 with the Toyota Aristo. Exclusive to the Japanese Domestic Market, the Aristo included the 3.0-liter inline-six 2JZ engine. This car lasted on the market until 2007 and is still a highly sought-after vehicle. Of course, a significant reason is the inclusion of the revolutionary Toyota engine.
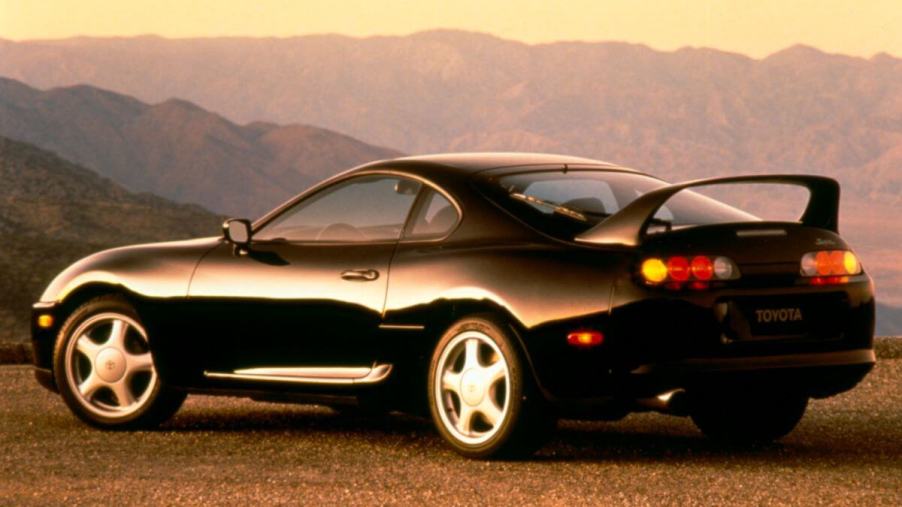
Despite the Aristo being first, the Supra is perhaps the most well-respected car to feature the Toyota 2JZ engine. Additionally, the fourth-generation Supra was the first U.S. vehicle to use it. The 1993 Toyota Supra came standard with a maximum output of 220 horsepower. However, a turbocharged version also produces a maximum output of 320 horsepower. The turbocharged version accelerates from 0 to 60 mph in 4.6 seconds.
Differences between the Toyota JZ series engines
There are a few differences between the Toyota 2JZ and the 1JZ that make it a more beloved powerhouse. Perhaps the most significant difference is that the 2JZ has a displacement of 3.0 liters, whereas the 1JZ is a 2.5-liter engine. Another big difference is that the 2JZ can withstand more than its smaller counterpart, thanks to its closed-deck cast iron block design. This means drivers could push the engine more and worry less about potential damage, which makes it a top choice for race cars.
People also prefer the Toyota 2JZ engine over the 1JZ because it has a longer stroke. Its longer stroke is valuable for a couple of reasons, the first being engines with longer strokes tend to produce better torque at lower RPMs. Additionally, a longer stroke often means better fuel economy as they have less surface area during combustion. For context, the 2JZ engine has a stroke length of 86 mm while the 1JZ is 83 mm. Still, the Toyota JZ series as a whole is unmatched.
The Toyota 2JZ has a vibrant legacy
Ask any car enthusiast, and they’ll tell you that the Toyota JZ series of engines has an important legacy. This is for many reasons. Perhaps the biggest is that the 2JZ powerhouse never had a true successor. Additionally, it never had any real competition while on the market. Toyota engineered the engine to abide by the aforementioned gentlemen’s agreement, but people could still modify it to be more powerful.
Therefore, the engine also has an impeccable legacy because Toyota made it easy to customize. The 2JZ isn’t a huge engine. This smaller size means people can add things like turbochargers more easily. This goes a long way because it also makes preparing cars for racing less of a daunting task. Overall, the 2JZ is one of the best engines of all time. It’s still highly regarded today and has outlived any option that ever came close to its status.